What is CVE-2025-24813?
CVE-2025-24813 is a critical path equivalence vulnerability in Apache Tomcat, with exploitation attempts by threat actors observed in the wild. The vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers without authentication under specific conditions, potentially leading to system compromise and sensitive data being exposed.
Given the high risk associated with this vulnerability and ongoing exploitation attempts, it is imperative to prioritize patching CVE-2025-24813 on your company's assets to mitigate potential attacks and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
The vulnerability affects Tomcat versions 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2, 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34, and 9.0.0. M1 to 9.0.98. Additionally, Insikt Groups analysis found that 8.5.x versions (specifically 8.5.0 to 8.5.98 and 8.5.100, with the exception of 8.5.99) are also vulnerable, though they were not included in the initial set of affected products by Apache.
Insikt Groups Assessment of CVE-2025-24813
CVE-2025-24813 stems from Tomcats handling of partial PUT requests and allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to conduct remote code execution (RCE), view security-sensitive files, and inject content into those files.
Exploitation involves two primary steps:
- The attacker sends a PUT request containing a Base64-encoded serialized Java payload to the server. This payload is designed to trigger RCE upon deserialization.
- The attacker then sends a GET request with a specially crafted JSESSIONID cookie referencing the malicious session, causing the server to deserialize the payload and execute arbitrary code.
However, successfully conducting RCE requires the following conditions:
- The default servlet must have write permissions enabled (disabled by default)
- Partial PUT support must be enabled (enabled by default)
- The application uses Tomcat's file-based session persistence with the default storage location
- The application includes a library that can be leveraged in a deserialization attack
If the following conditions are true, attackers can view sensitive security files and inject content into those files:
- The default servlet must have write permissions enabled (disabled by default)
- Partial PUT support must be enabled (enabled by default)
- The target URL for sensitive uploads resides within a sub-directory of the public uploads directory
- The attacker is aware of the filenames of the security-sensitive files being uploaded
- The security-sensitive files are uploaded using partial PUT requests
As such, only a limited number of Tomcat instances are likely to be affected by the configuration required for exploitation. For example, a GitHub code search query to check for the write permissions condition (
Cybersecurity firm Greynoise has identified six malicious IP addresses attempting to exploit CVE-2025-24813, targeting systems in the US, Japan, Mexico, South Korea, and Australia. However, Insikt Group has not identified any evidence of successful exploitation or any evidence of known threat actors exploiting the vulnerability. At the time of writing, there were 378,444 exposed instances on Shodan. The specific versions are disclosed in the title and body of the servers responses.
| Malicious IP Address | Source Location | Target Location |
| 203.160.68[.]24 | Hong Kong | US |
| 176.65.138[.]172 | Germany | Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Pakistan, Taiwan |
| 38.126.114[.]186 | US | India, Japan, Mexico, US |
| 188.213.161[.]98 | Italy | Japan, South Korea |
| 140.143.182[.]115 | China | US, Australia, Mexico, South Korea |
| 196.240.54[.]120 | Latvia | US |
Table 1: Malicious IP addresses attempting to exploit CVE-2025-24813 (Source: Greynoise)
Multiple proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits have been published, including by Palo Alto Networks and GitHub user iSee857, which can be found in the Validation URL section of this note. These public exploits increase the likelihood of ongoing exploitation attempts. Insikt Group did not test these PoCs for efficacy or accuracy.
Indicators of compromise (IoCs):
- Presence of unexpected JSP files in the web server root directory
- External POST or GET requests targeting suspicious JSP files
- Occurrence of unexpected PUT requests in web server logs
- Evidence of malicious payloads being delivered via PUT requests
- Triggered WAF rules indicating attempts to upload or execute unauthorized files
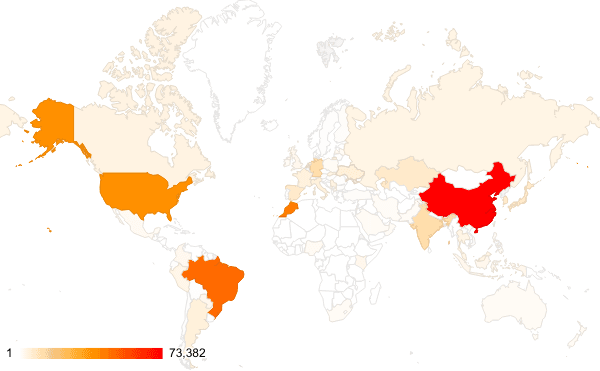 Figure 1: The majority of exposed Tomcat instances on Shodan are geolocated in China, Brazil, Morocco, and the US (Sources: Shodan, Recorded Future)
Figure 1: The majority of exposed Tomcat instances on Shodan are geolocated in China, Brazil, Morocco, and the US (Sources: Shodan, Recorded Future)
Recommended Actions for CVE-2025-24813
Users should upgrade to version 11.0.3, 10.1.35 or 9.0.99. For end-of-life (EoL) 8.5.x versions, users should upgrade to a supported branch of Apache Tomcat. If upgrading is not immediately possible, users should implement network-level controls to restrict access to the Tomcat server.
How Recorded Future Can Help:
- Insikt Group - Download the attached YAML file in this blog post to access a Nuclei template created by Insikt Group for CVE-2025-24813 that enables defenders to test potentially vulnerable Apache Tomcat instances prior to the patched version.
- Attack Surface Intelligence - Identify internet-facing assets vulnerable to CVE-2025-24813.
- Vulnerability Intelligence - Gain helpful context on CVE-2025-24813 to aid in patching and prioritization discussions.
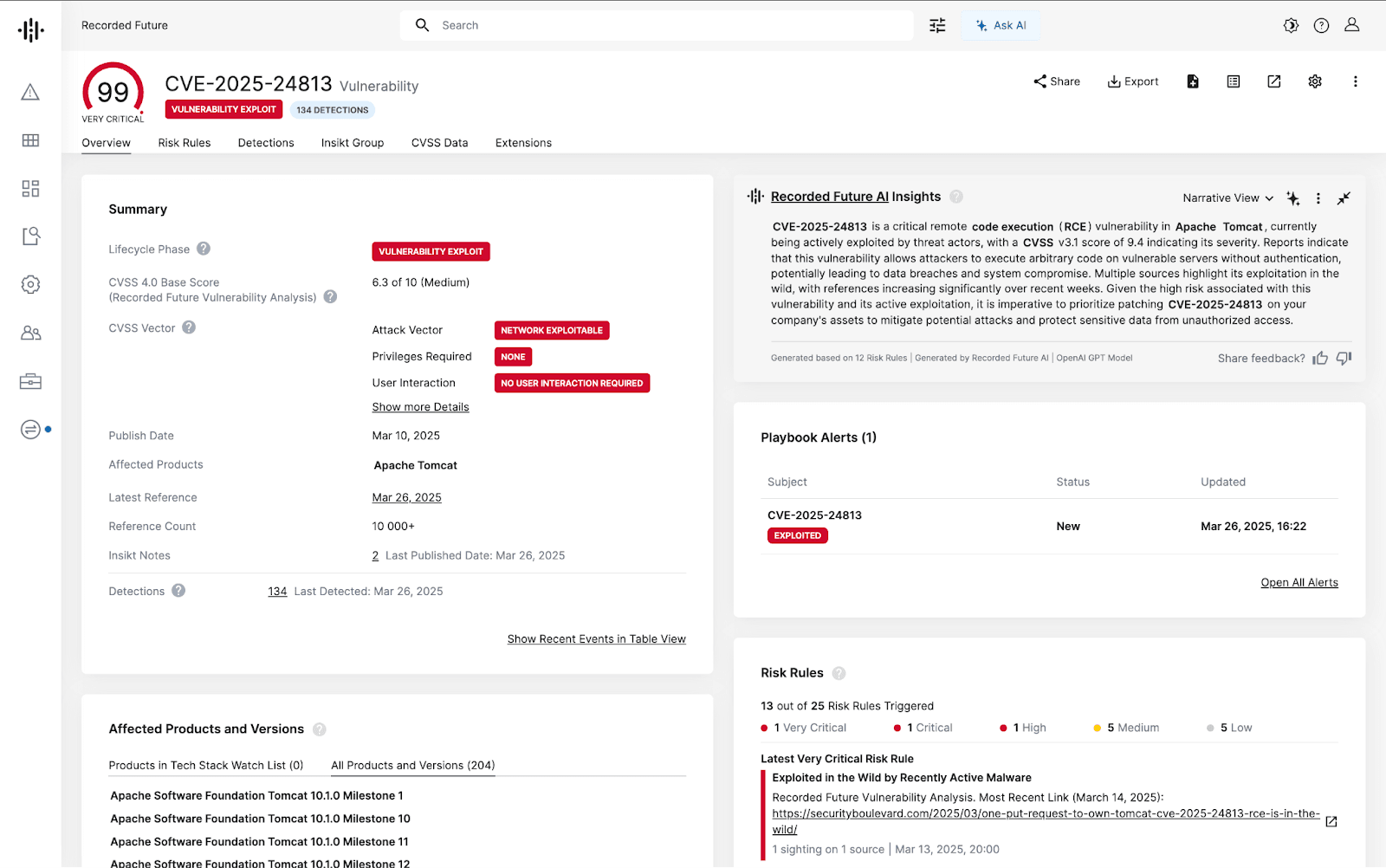 Figure 2: Vulnerability Intelligence Card for CVE-2025-24813 in Recorded Future (Source: Recorded Future)
Figure 2: Vulnerability Intelligence Card for CVE-2025-24813 in Recorded Future (Source: Recorded Future)
 Figure 3: Signature for CVE-2025-24813 in Recorded Future Attack Surface Intelligence (Source: Recorded Future)
Figure 3: Signature for CVE-2025-24813 in Recorded Future Attack Surface Intelligence (Source: Recorded Future)
About Insikt Group:Recorded Futures Insikt Group threat research team is comprised of analysts, linguists, and security researchers with deep government and industry experience.
Insikt Group publishes threat intelligence to the Recorded Future analyst community in blog posts and analyst notes.
Source: RecordedFuture
Source Link: https://www.recordedfuture.com/blog/apache-tomcat-cve-2025-24813-vulnerability-analysis